A blog about Science & Nutrition
-

Vitamin D: Deficiency, Dosage, and Sources
Vitamin D or “calciferol” is a fat-soluble vitamin that is naturally available in some foods. It is also produced within the body when ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight strike the skin and trigger vitamin D synthesis. Supplements of vitamin D are also available. Difference between Vitamin D3 and Vitamin D2 Vitamin D has two major…
-

Vitamin C Benefits
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid is a water soluble vitamin. This vitamin is naturally present in some foods and it is not produced inside the human body. So, it is an essential dietary component. Health Effects of Vitamin C Recommended Daily Dose Average daily recommended amount depends on age, which tabulated below. Life Stage Recommended…
-

Blood Glucose: Control it with Exercise
Sedentary lifestyle is spreading across the globe. Workplace routine, unavailability of exercise places, high screen time, and luxury lifestyle has contributed to increased sedentary time. Sedentary lifestyle increases the likelihood of high levels of glucose in blood in both healthy adults and diabetic patients. Can Exercise Effects Blood Glucose? Exercise and physical activity are major…
-

How to Control Blood Sugar Spikes
Blood sugar or glucose is the concentration of glucose that is present in blood at all times. In fed state, most of glucose in blood comes through diet. In fasting state, glucose concentration in blood is maintained either by using glycogen stored in lever and muscles (glycogenolysis) or by gluconeogenesis. Normal level of blood sugar…
-
Gut Microbiome: Crucial for Health
The collection of microorganisms that colonizes the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is called gut microbiome. Development of microbiome starts from birth and changes in microbiome takes place with life event such as illness, antibiotic treatment and changes in diet. Approximately, 100 trillion microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa) exist in the human gastrointestinal tract. The bacteria in the microbiome help to: The Role of Gut Microbiome Gut microbiome…
-

Trans Fatty Acids
Trans-fats or Trans fatty acid is a type of unsaturated fat, that occurs naturally and large proportion is industrially produced. Trans-fat is produced by reacting unsaturated fat with hydrogen gas in the presence of catalyst in a process called partial hydrogenation. Partial hydrogenation of oil gives it a semisolid to solid texture (depending upon the…
-
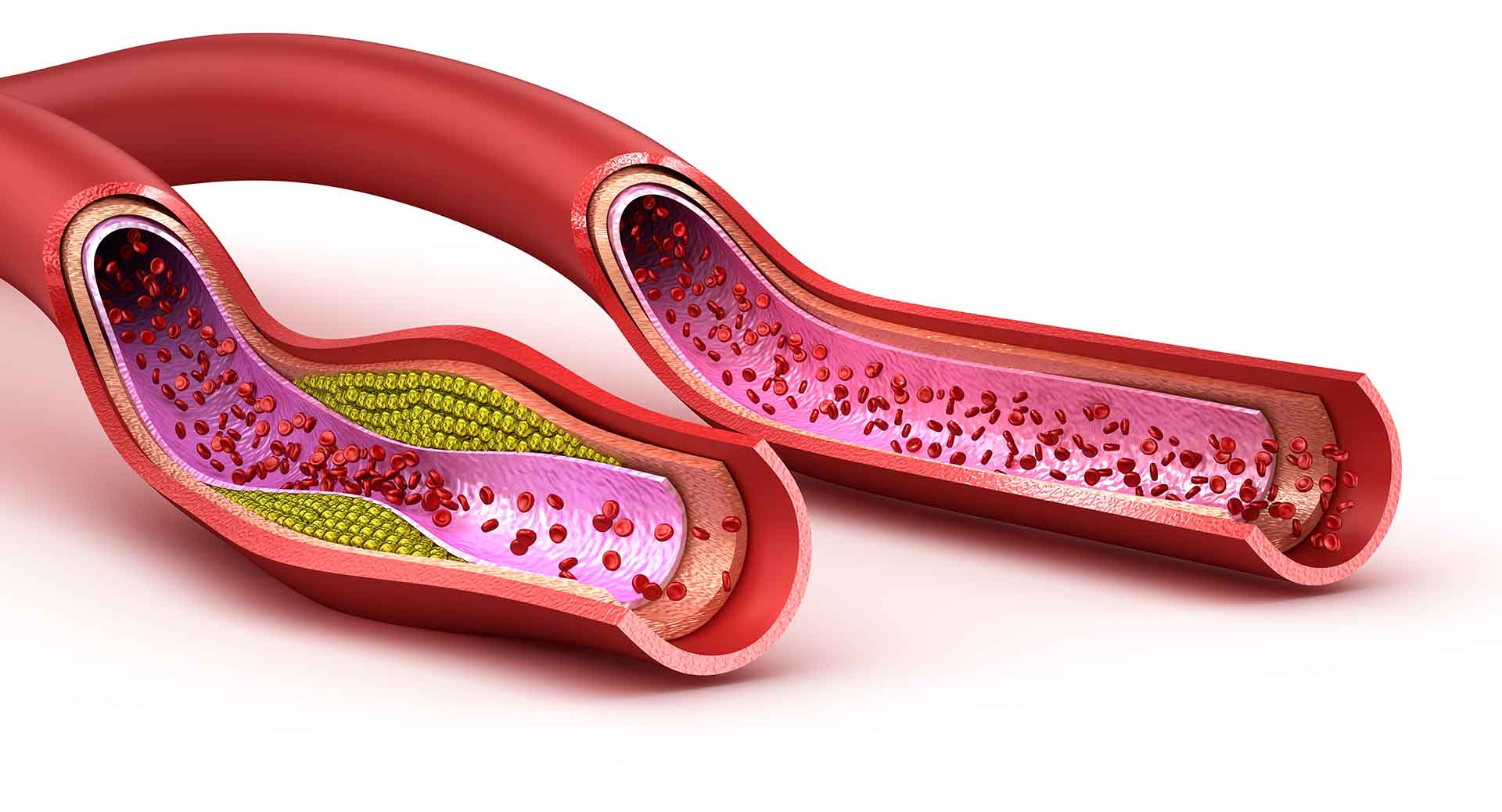
How to Reduce Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy substance. Our body needs it to build cells, produce vitamins, hormones and bile acids. Cholesterol is not a bad substance when it is within certain limits. We get cholesterol from our diet known as dietary cholesterol. Our body makes most of cholesterol in liver and maintains a healthy balance of cholesterol…
-

Eggs: Are They Healthy or Not
Eggs are nutritional dense food that can supply every nutrition required by the body except fiber. White part of an egg is a complete protein that contain all nine essential amino acids required by human body. Egg white does not contain fat, all of the fat is available in yolk. Yolk is the nutritional dense…
-

Intermittent Fasting: What are the Benefits
Intermittent fasting or simply fasting means that you do not voluntarily eat for a period of time each day or week. Duration of fasting varies from twelve hours to days. Shorter duration fast can be carried out more frequently. For example in 14/10 fast, you fast for 14 hours and eat all your meals within…
-

Dietary Fiber: Essential for Healthy Life
Dietary fiber is non-digestible carbohydrate that passes through the small intestine without digestion or absorption however, it passes through the large intestine with partial or complete fermentation. Fiber is commonly classified as soluble and insoluble, depending upon its solubility in water. The amount of soluble and insoluble fiber varies in different plant foods. Soluble…